
False Codling Moth (FCM), Thaumatotibia leucotreta, is a high-risk pest that threatens the economic value of numerous high-value crops, including flowers and fruits. Its ability to thrive across multiple hosts and diverse environments has made it a major quarantine concern for importing countries. With the April 26 compliance deadline fast approaching, growers and exporters face increased pressure to demonstrate effective FCM management.
In response, agrochemical companies are striving to help combat the menace through targeted pest management solutions. Corteva Agriscience is at the forefront of this effort, offering a range of products specifically formulated to manage FCM. These include Uphold™ 360SC, Tracer™ 480SC, and Delegate™ 250WG each developed to deliver effective control while supporting sustainable production and compliance with export market requirements.
What is False Codling Moth (FCM)
FCM is a pest of significant economic importance affecting valuable crop commodities: flowers, Pepper, Nut and Fruit crops. It is an endemic pest to sub-Saharan Africa, its polyphagous nature with over 70 plant hosts, ability to adapt to a variety of hosts and environmental conditions make it of significant quarantine concern in other areas of the world.
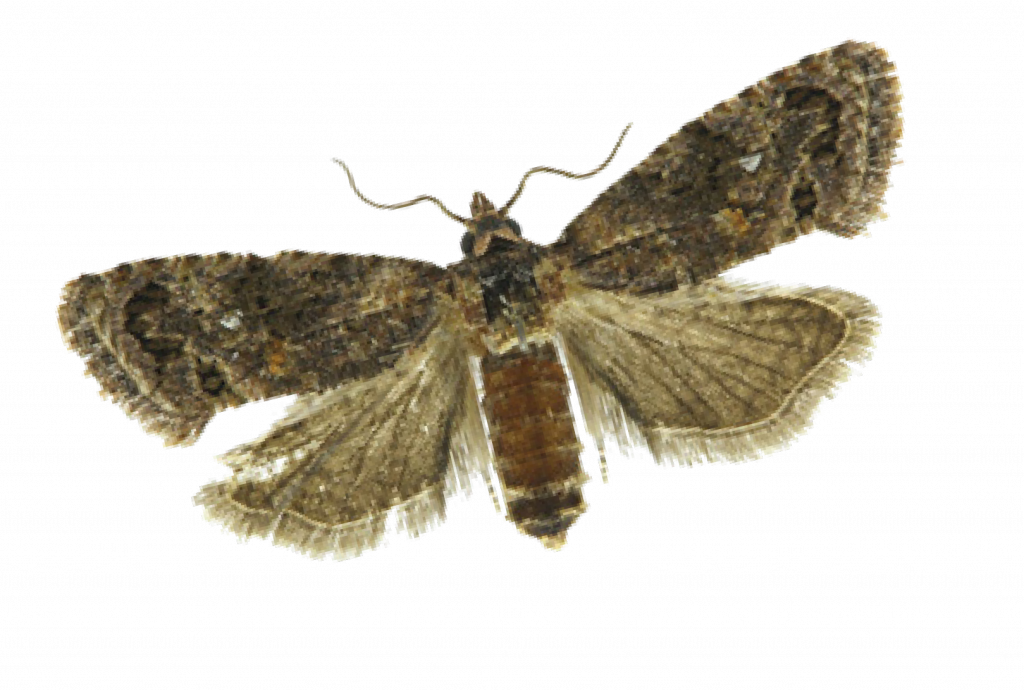

It’s a Lepidoptera, with its larvae being the most devastating stage of FCM.



FCM Adults Characteristics:
- Length: 7 – 10 mm;
- Wingspan: 15-20 mm (depending on sex)
- Colors: grey, brown, black, and orange brown
- Crest on top of the thorax
- Black C-markings on forewings is dark in colour.
- Two white dots on the forewings
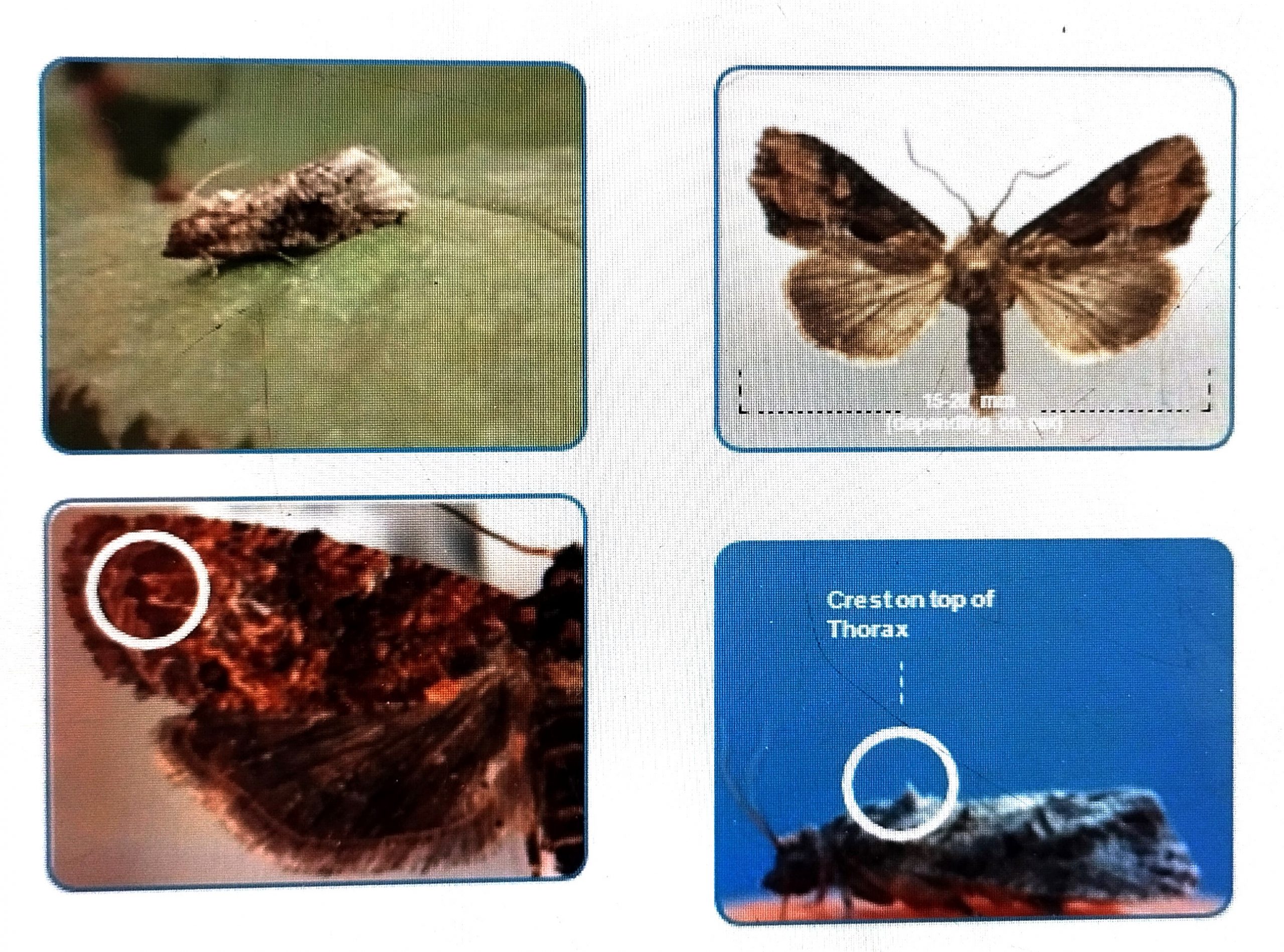

Major Comparison between Male and Female FCM
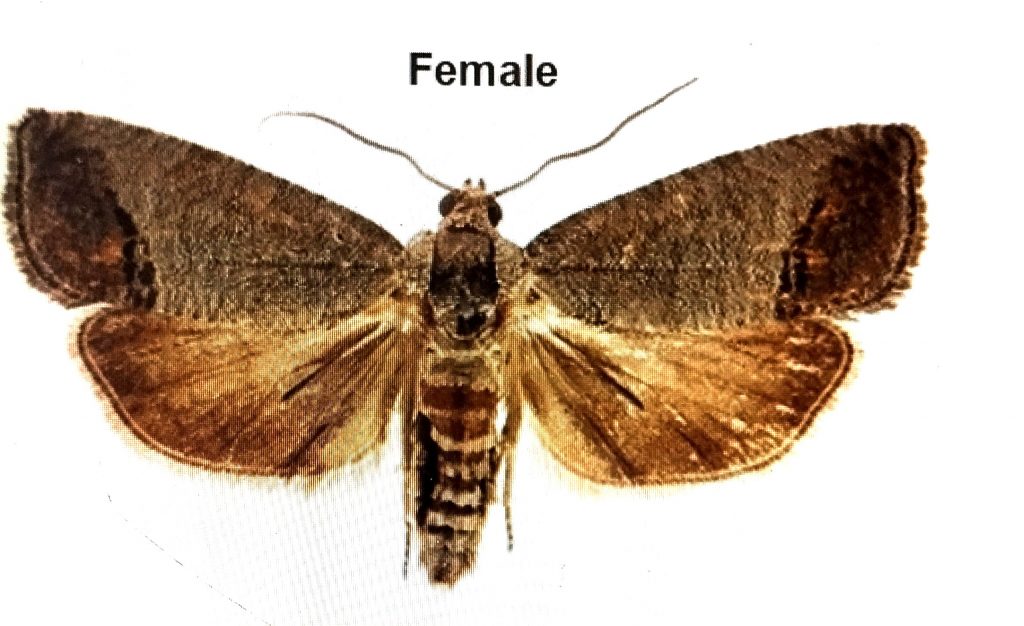
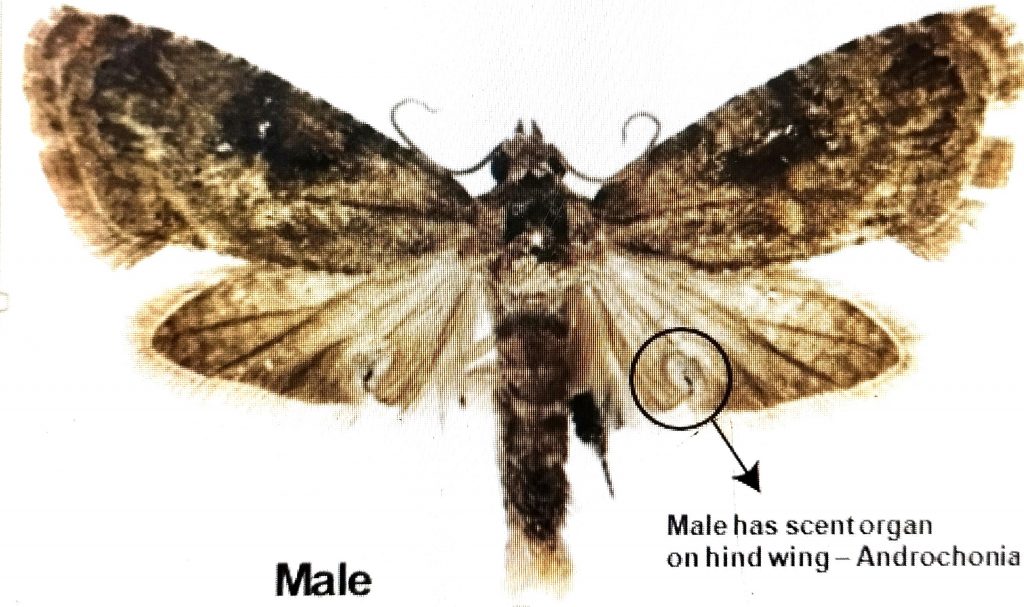

- Female has no scent organ on hind wing)
- Male has scent organ on hind wing – Androchonia
Fcm Eggs Stage
- Laid singly
- Usually on tender parts/flower buds
- Size: 0.9 mm long
- Duration: 9-12 days winter; 6-8 days in summer

Eggs are whitish and oval in shape. Eggs turn reddish when about to hatch

Larvae Stage
- 1st to 4th Instar has whitish to creamish body
- Brownish to dark head

- 5th instar the body is pinkish in colour and head is darkish in colour
- All instars have 4 prolegs on the underside of the larval stage

Pupa Stage
- Colour: Cream yellow to dark brown

- Female are larger than the Male Male has 2 knobs side by side
- Both male and female have a serrated posterior ending
FCM Management
Must involve an integrated approach in all stages of production and processing through training of the stakeholders.
Effective Scouting & Monitoring
The scouts must be aware of the following for successful scouting: Plant and pests’ biology.
- Pests’ life cycles.
- Range of host plants.
- Type of damage to the crop attributable to the pest.
Lepidoptera Management Solutions
Physical Control Measures
- Exclusionary measures by use of insect nets
- Monitoring by use of FCM Pheromones lures & traps/dispenser – Mating disruption, Attract & kill technique,
- Sterile insect technique
Cultural Control Measures
- Collect and burn debris and unwanted plant parts,
- Crop rotation
- phytosanitary measures- Field hygiene including removal of crown gall
- Removal of alternative hosts
- Removal and proper disposal of the affected plant parts.
Biological Control Measures
- Controlled releases of FCM egg parasitoids (Trichogramma cryptophlebiae), application of the CrleGV virus where commercially available
Chemical Control Measures
- Consider MoA for resistance management
- Ensure proper coverage
- Alternate approved insecticides of different MOA with proofed efficacy on the larvae stage as well as adults.
Systems Approach Control Measures
Specific country phytosanitary teams jointly with other stakeholders have developed a systems approach consisting of three key measures:
- Preharvest controls and measurements and postpicking sampling, inspection, and packinghouse procedures
- Postpacking sampling and inspection; and
- Shipping conditions.
The key CORTEVA solutions for FCM are;
- Uphold 360 SC – eggs up to L5 larval stage, fecundity on male and female adults
- Delegate 250 WG – neonates – L5 larvae, adults
Ensuring compliance with FCM management standards is crucial to maintaining export opportunities and protecting market access. Growers and exporters must act now, not only to meet regulatory requirements but to safeguard the long-term viability of their crops in an increasingly competitive global market.
